Watershedding Segmentation Parameters
Appropriate parameters must be chosen to properly use the watershedding segmentation module in tobac. This page gives a brief overview of parameters available in watershedding segmentation.
A full list of parameters and descriptions can be found in the API Reference: tobac.segmentation.segmentation().
Basic Operating Procedure
The tobac watershedding segmentation algorithm selects regions of the data field with values greater than threshold and associates those regions with the features features detected by feature detection (see Feature Detection Basics). This algorithm uses a watershedding approach, which sets the individual features as initial seed points, and then has identified regions grow from those original seed points. For further information on watershedding segmentation, see the scikit-image documentation.
Note that you can run the watershedding segmentation algorithm on any variable that shares a grid with the variable detected in the feature detection step. It is not required that the variable used in feature detection be the same as the one in segmentation (e.g., you can detect updraft features and then run segmentation on total condensate).
Segmentation can be run on 2D or 3D input data and with 2D or 3D feature detection output, but segmentation on 3D data using a 2D feature detection field requires careful consideration of where the vertical seeding will occur (see Level).
Target
The target parameter works similarly to how it works in feature detection (see Threshold Feature Detection Parameters). To segment areas that are greater than threshold, use target='maximum'. To segment areas that are less than threshold, use target='minimum'.
Threshold
Unlike in multiple threshold detection in Feature Detection, Watershedding Segmentation only accepts one threshold. This value will set either the minimum (for target='maximum') or maximum (for target='minimum') value to be segmented. Note that the segmentation is not inclusive of the threshold value, meaning that only values greater than (for target='maximum') or smaller than (for target='minimum') the threshold are included in the segmented region.
Projecting 2D Spatial Features into 3D Segmentation
When running feature detection on a 2D dataset and then using these detected features to segment data in 3D, there is clearly no information on where to put the seeds in the vertical. This is currently controlled by the level parameter. By default, this parameter is None, which seeds the full column at every 2D detected feature point. As tobac does not run a continuity check, this can result in undesired behavior, such as clouds in multiple layers being detected as one large object.
level can also be set to a slice, which determines where in the vertical dimension (see `Vertical Coordinate`_) the features are seeded from. Note that level operates in array coordinates rather than physical coordinates.
Projecting 3D Spatial Features into 2D Segmentation
When running feature detection on a 3D dataset and then using these detected features to segment data in 2D, the vertical coordinate is ignored. In case of vertically overlapping features, the larger Feature value is currently seeded.
Projecting 3D Spatial Features into 3D Segmentation
When running feature detection on a 3D dataset and then using these detected features to segment data in 3D, there are currently two options for determining how to seed the watershedding algorithm: column seeding (set by seed_3D_flag='column') and box seeding (set by seed_3D_flag='box'). We generally recommend box seeding when running feature detection and segmentation in 3D.
Column seeding (seed_3D_flag='column') works by setting seed markers throughout some or all of the vertical column at all detected feature centroids (i.e., one column per feature detected). While the default behavior is to seed throughout the full vertical column, the vertical extent of the seeds can be set by passing a slice into the level parameter. Note that level operates in array coordinates rather than physical coordinates.
Box seeding (seed_3D_flag='box') sets a cube or rectangular seed markers around the detected feature in 3D space. The marker size is user defined (in array coordinates) by seed_3D_size as either an integer (for a cube) or a tuple of (int, int, int), ordered (vertical, hdim_1, hdim_2). Note that seed_3D_size must be an odd number to avoid the box becoming biased to one side. If two seed boxes overlap, the seeded area is marked with the closest feature centroid.
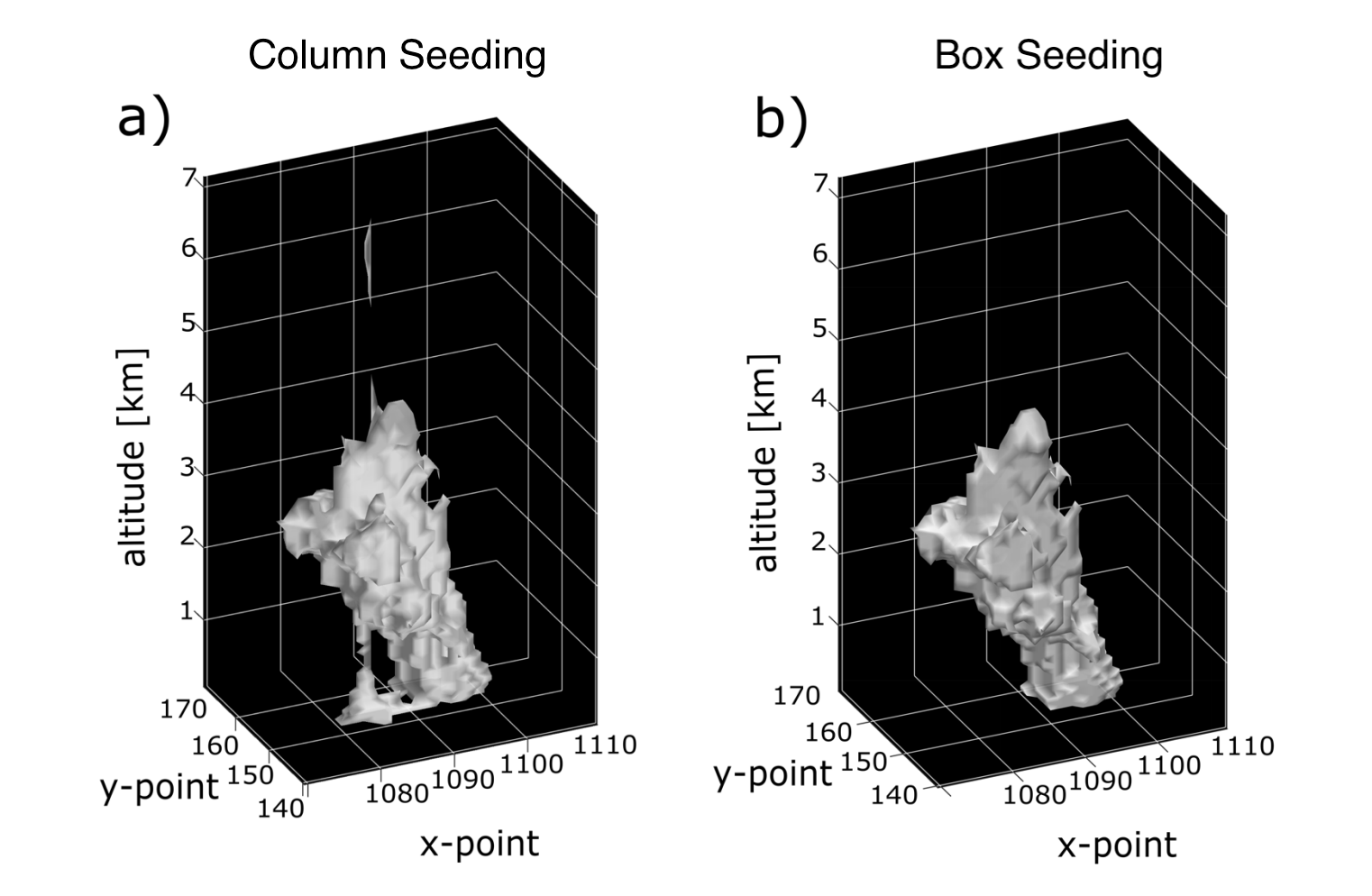
An example plot from a numerical model simulation showing the real-world difference between column and box seeding with a tilted feature. As this image demonstrates, box seeding is typically recommended for 3D data.
Maximum Distance
tobac’s watershedding segmentation allows you to set a maximum distance away from the feature to classify as a segmented region belonging to that figure. max_distance sets this distance in meters away from the detected feature to allow it to be considered part of the point. To turn this feature off, set max_distance=None.